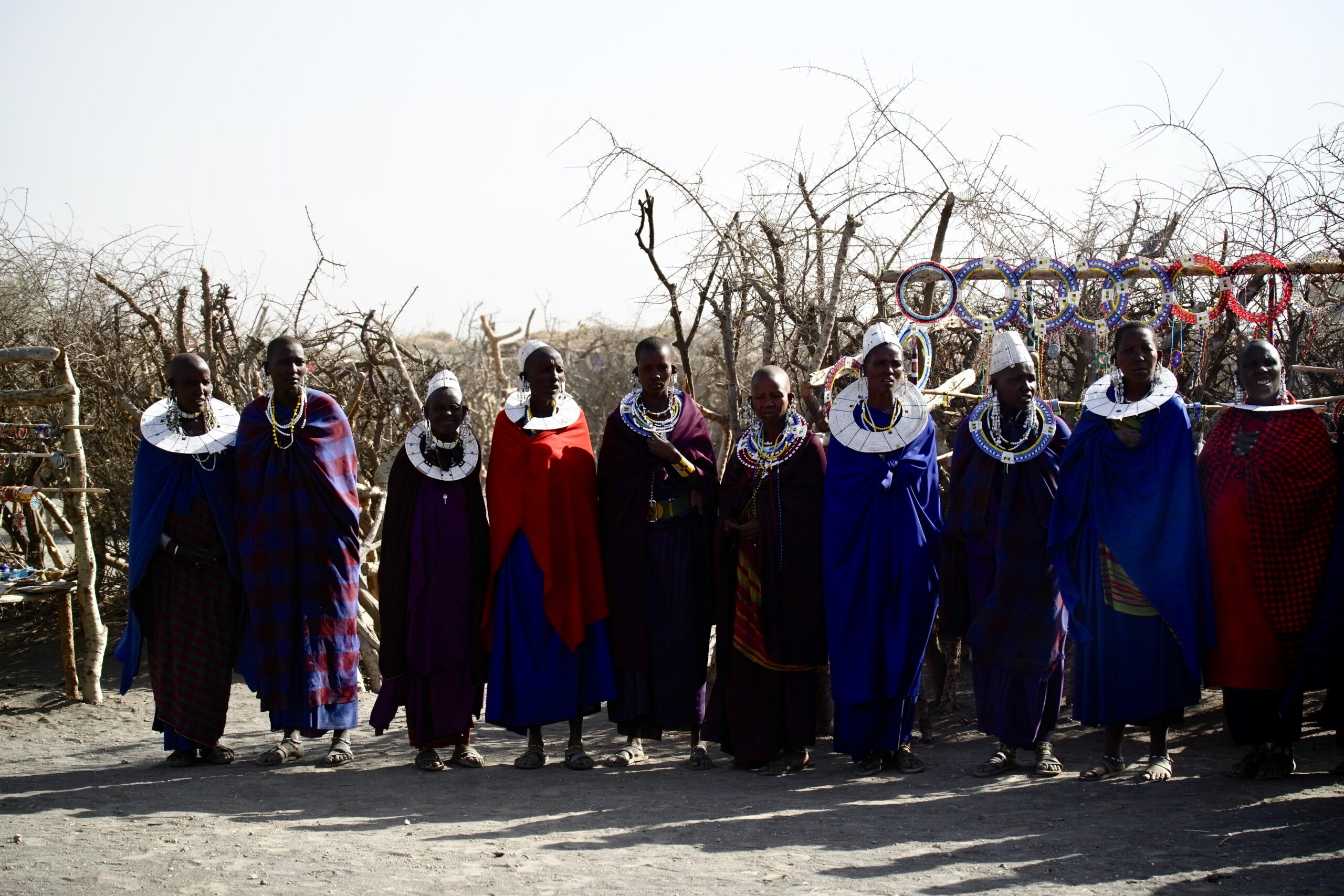
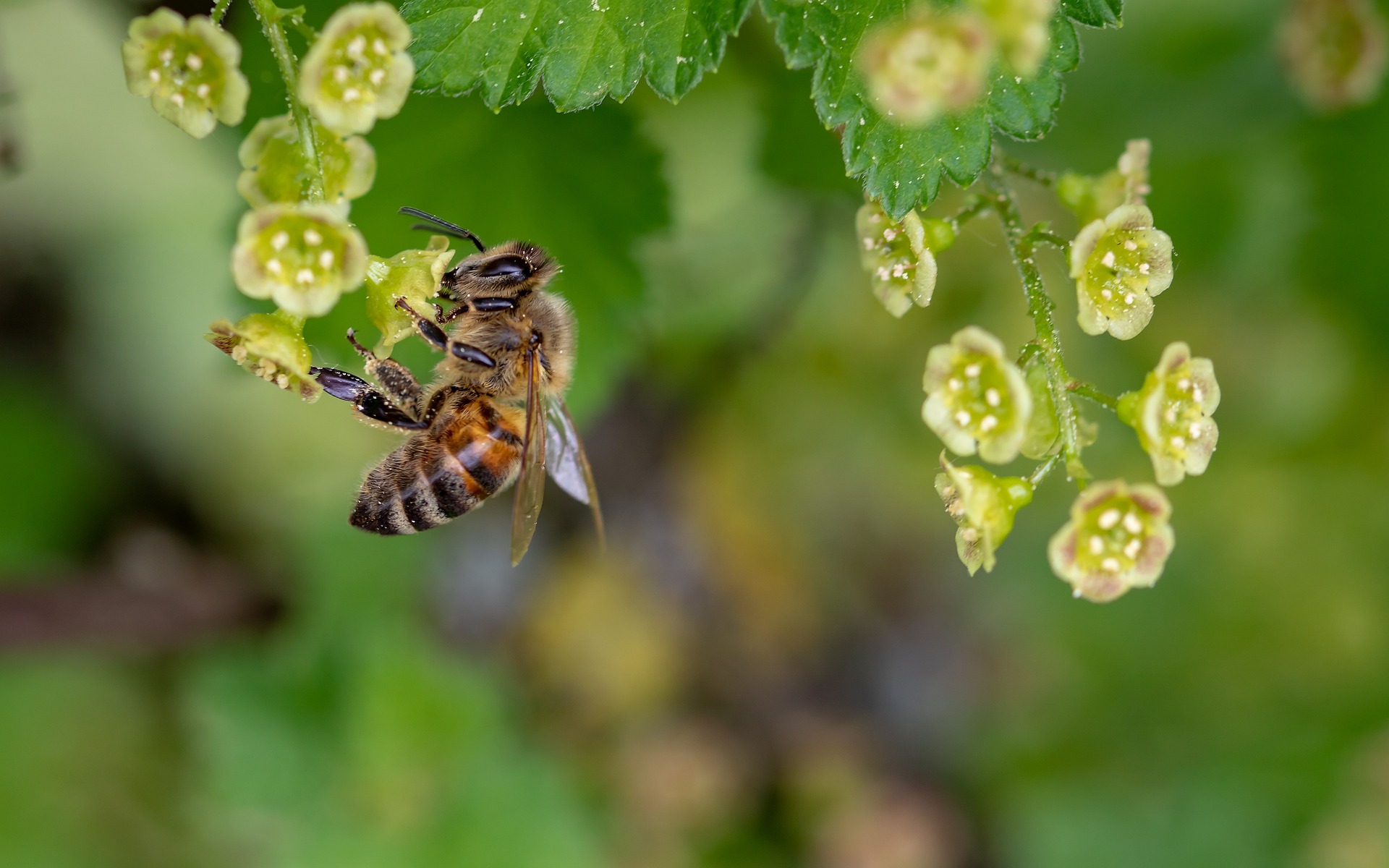
Kenya’s ecological diversity ranges from lowland and mountain forests to wooded and open grasslands, semi-arid scrubland, dry woodlands, inland aquatic and coastal and marine ecosystems. The country is taking strategic actions to address threats and promote sustainable utilization of biodiversity.
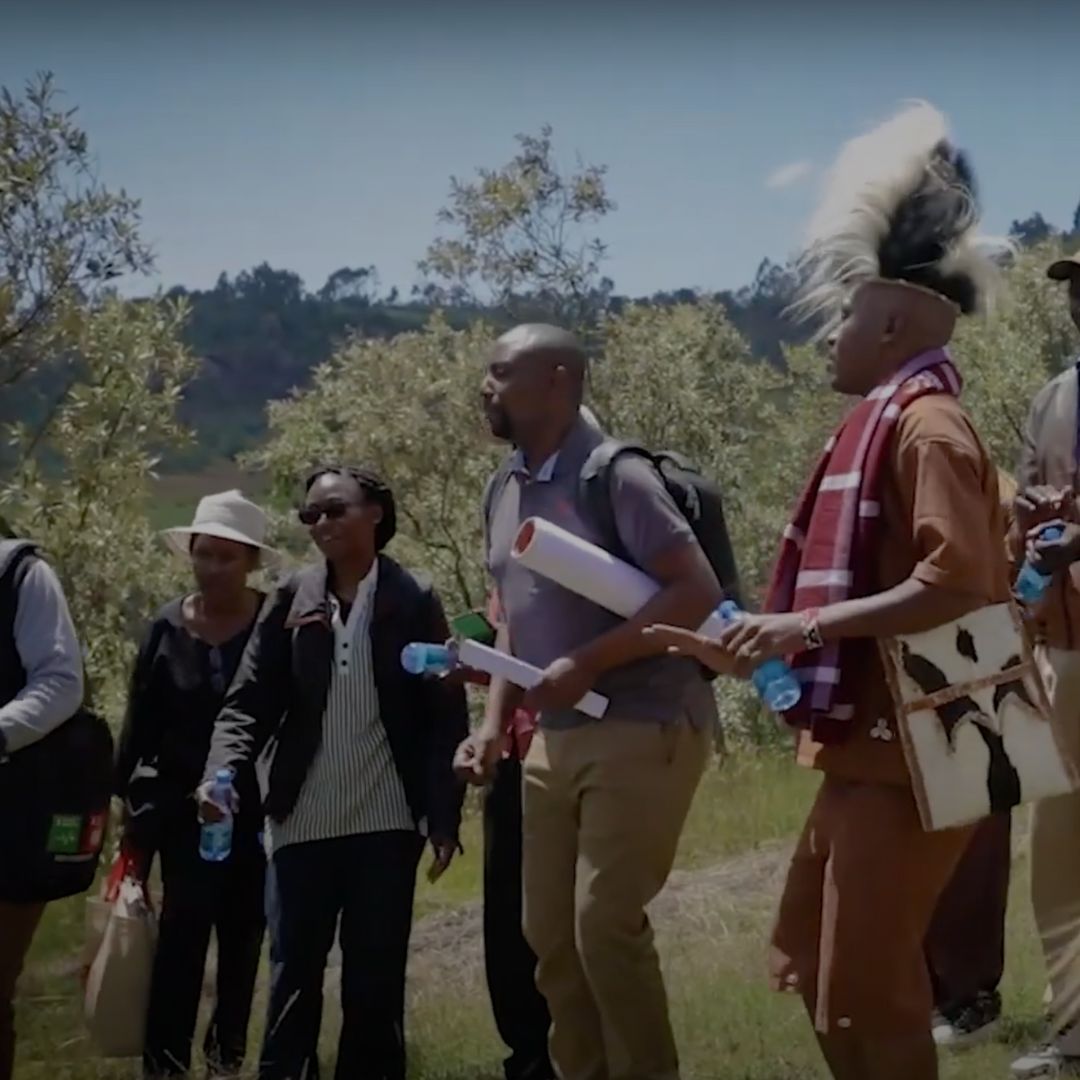
- In May 2019, the Ministry of Environment and Forestry in Kenya hosted the Anglophone Africa Regional Trialogue in Nairobi to raise awareness of the key messages of the two interlinked IPBES Thematic Assessment Reports on Pollinators, Pollination and Food Production and Land Degradation and Restoration.
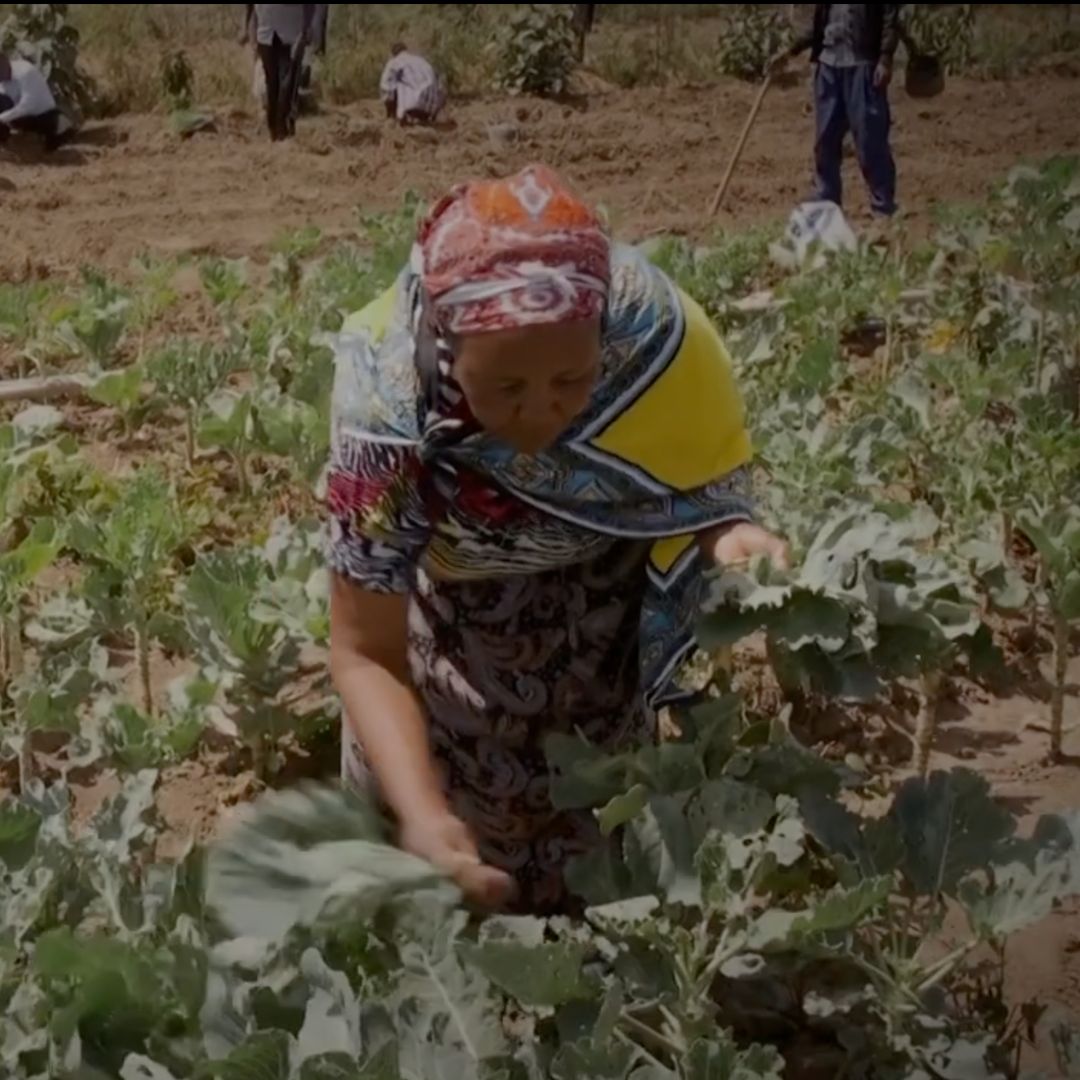
- The country received support from BES-Net to contribute to national efforts addressing land degradation through agroforestry practices that utilize pollinator-friendly crops and promote land restoration.
- Under BES-Net Phase II, Kenya received catalytic support through the BES Solution Fund to implement key priority actions identified during the Trialogue.
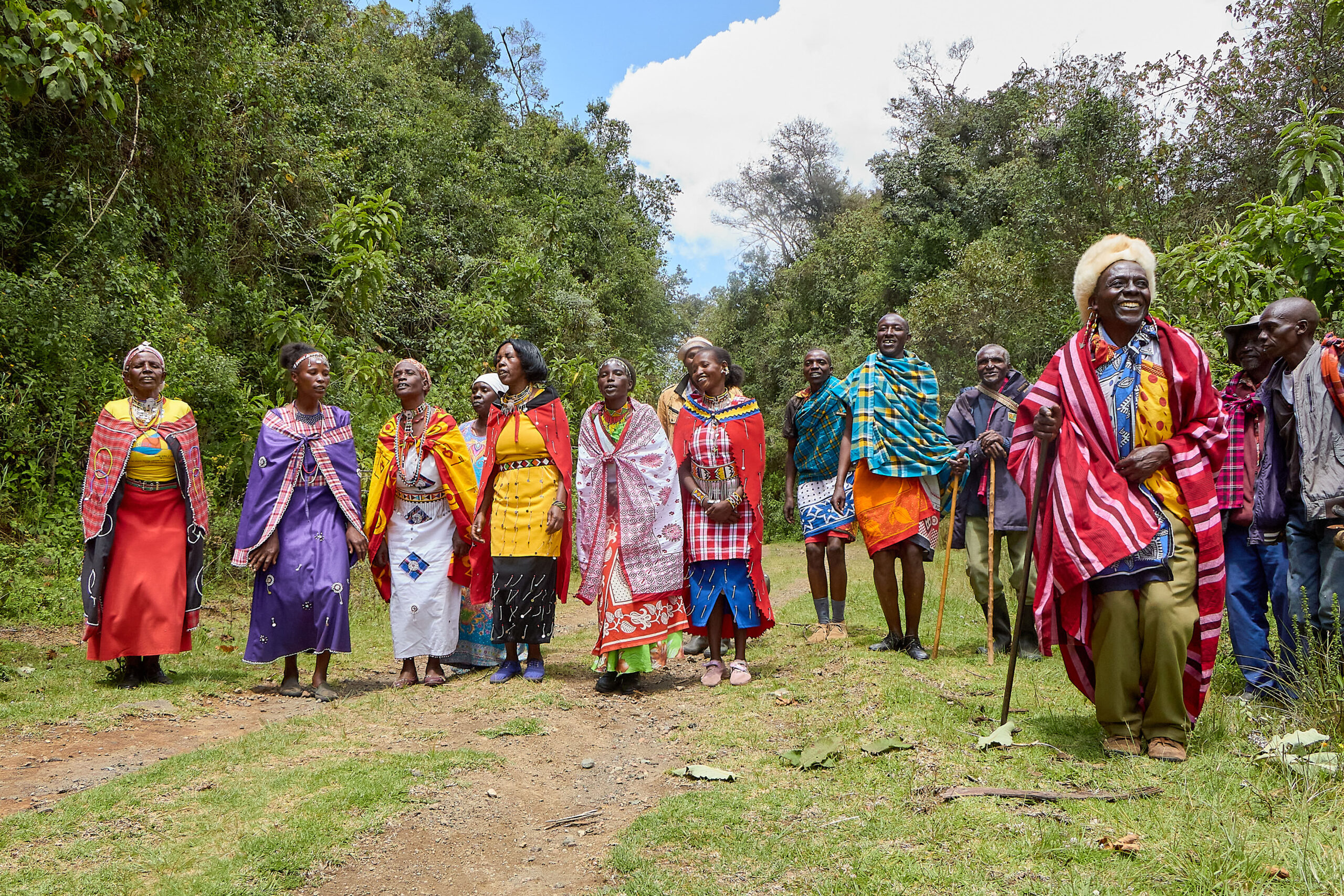
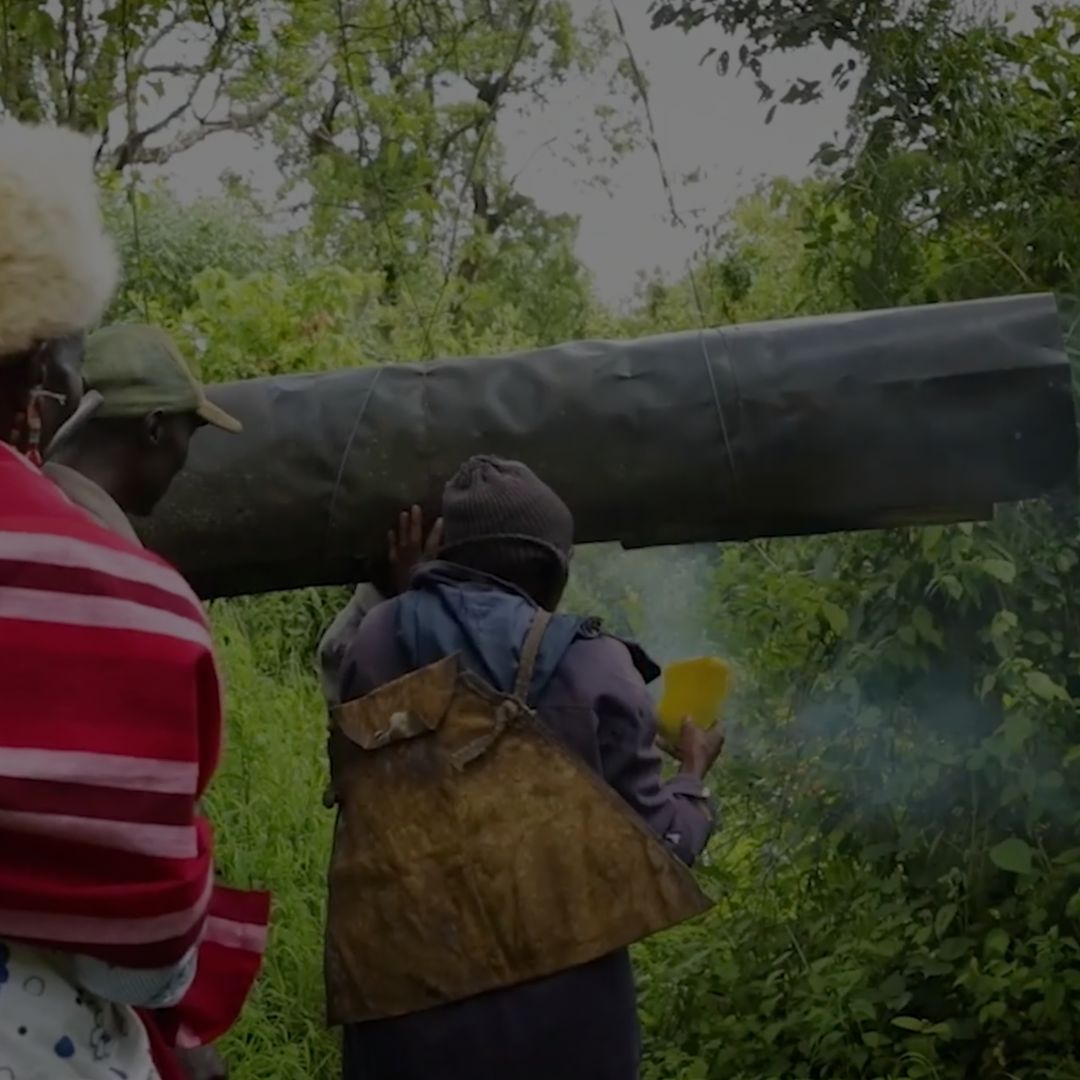
- Through the support concluded at the end of 2024, local communities (including Indigenous Peoples such as the Ogiek People group and youth) were actively engaged in efforts towards pollinator management, land restoration and the promotion of Indigenous and local knowledge and intergenerational learning in pollinator conservation and sustainable land management. Some key products developed include two documentaries, a photo essay and a booklet on Indigenous and local knowledge related to pollinators and sustainable land management practices by the Ogiek and local communities in the Eburu ecosystem as part of the documentation of such an important knowledge source.
Implementing agencies: UNDP Kenya; Kenya National Trialogue secretariat